Instructor Led Training
- World-Class Instructors
- Mentor Support
- Instant doubt clearing
 United States
United States
 India
India United States
United States United Kingdom
United Kingdom Australia
Australia Canada
Canada Nigeria
Nigeria Others
Others
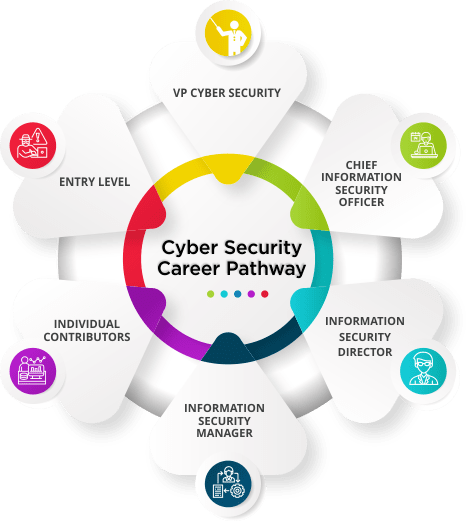
Become the Cybersecurity Leader of Tomorrow

Students Placed

Highest Salary

Average Salary Hike

Hiring Partners
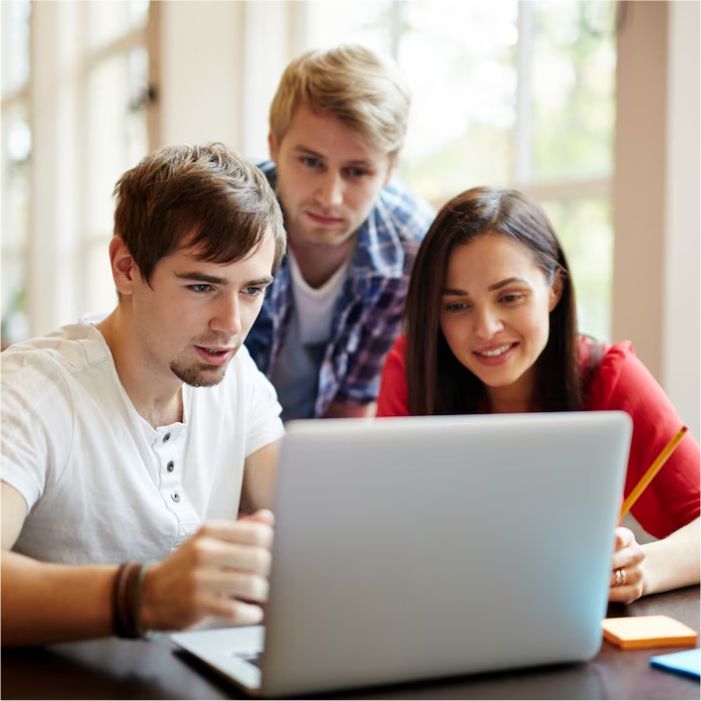
Looking to dive into the world of cybersecurity? Look no further than the best cyber security courses available at Learning Saint. With the rise in cyber threats, obtaining a professional cyber security certification is paramount. Our advanced-level certification training offers comprehensive coverage of essential concepts, preparing you to tackle cyber challenges head-on.
At Learning Saint, our programs are specially designed to stand out among the best online cyber security certificate programs, featuring multiple live projects overseen by globally renowned trainers. Engage in live online sessions, meticulously designed to simulate real-world scenarios. Our examination preparation ensures you're ready to ace industry-standard certifications, recognized worldwide.
Immerse yourself in over 200 industry live projects, providing invaluable hands-on experience. Through real-world projects and case studies, you'll develop the skills needed to safeguard digital assets effectively. Our robust Learning Management System facilitates seamless learning, accessible anytime, anywhere.
Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting, our cybersecurity boot camp equips you with the knowledge and expertise demanded by today's cybersecurity landscape. Don't settle for less. Join the ranks of certified cyber defenders and embark on a fulfilling career securing the digital realm.
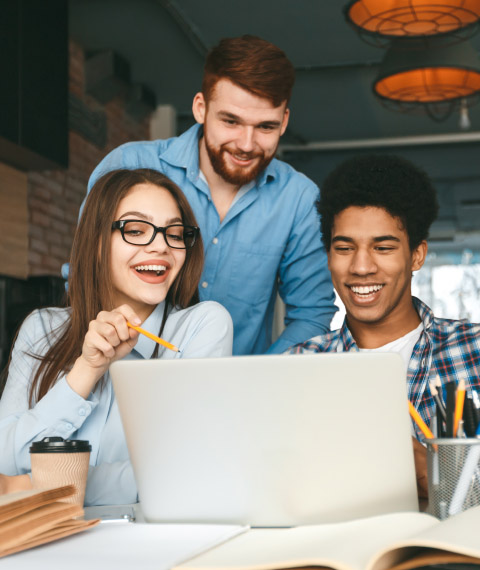
Don’t miss this opportunity to advance your career in cyber security. Enroll in Learning Saint’s Cyber Security Master Program Training & Certification and become a cyber guardian of the digital world. Our master’s program in Cyber Security is specially designed to make you an expert in this IT domain by teaching you various techniques and concepts, such as malware threats, trojans, cryptography, IAM, security operations, BIA, etc.
Throughout the program, students are prepared to obtain the best cybersecurity certifications available, ensuring industry recognition and validation of their expertise. From the best cyber security schools online, participants benefit from a cutting-edge curriculum delivered by seasoned professionals and experts in the field. The coursework covers a wide array of topics, including network security, cryptography, ethical hacking, and risk management.
For beginners, our cybersecurity boot camp offers an immersive learning experience, laying the foundation for a successful career in cybersecurity. With a focus on practical skills and real-world scenarios, students emerge ready to tackle cyber threats head-on. Alongside the program, students can pursue the best cyber security certifications for beginners, setting them on the path to becoming highly sought-after professionals.
Upon completion, graduates are equipped with the knowledge and credentials to pursue top cybersecurity certifications, further solidifying their expertise in the field. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to join the ranks of cybersecurity professionals making a difference in today’s digital landscape.
| Coverage | Courses | Mode of training |
| Security Fundamentals | CompTIA Security+ 501 | Live Virtual Classroom |
| Offensive Security | CEH | Live Virtual Classroom |
| Security Systems Architecture | CISSP | Live Virtual Classroom and Online Self-paced Learning |
| Cloud Security Architecture | CCSP | Live Virtual Classroom and Online Self-paced Learning |
| Electives | ||
| Networking Concepts | CompTIA Network+ | Online Self-paced Learning |
| Security Teams Management | CISM | Online Self-paced Learning |







Policies of personal security
Threat modeling
Risk considerations
Privacy protection
Ownership
MLOps
Data Wrangling
Requirements handling
Physical security
Security evaluation models
Network attacks
Security Auditor
Mechanism of authentication
Security architecture
In this first module, you will learn the basics of ethical hacking that are essential for the CEH exam.
Overview of Information SecurityMoving ahead in this Ethical Hacking course, you will master the first phase of ethical hacking, i.e. Footprinting and Reconnaissance
Concepts of FootprintingYou will have the opportunity to participate in a number of cases where you will get first-hand experience as a member of the ethical hacking team. You will assist in anticipating and preventing cybercrimes as well as identifying threats and data breaches.
Cracking WifiIn this project, you will learn a lot about WiFi cracking. You will use a variety of pertinent tools, technologies, and techniques to crack WiFi. You will learn how to break into different WiFi routers. The WPA/WPA2 are usually used.
Improvement of Auditing in the RestaurantThe project gives you the knowledge you need to learn how to improve any restaurant’s security system as needed. You will primarily employ a variety of techniques, including system resilience and the implementation of KPIs.
Data Security of a BPO FirmYou will understand the BPO firm’s data security. Working with data that has been generated by machines, you will search for irregularities, threats, and other things like suspicious activity. Additionally, the Splunk SIEM tool will be used to manage a sizable database.
Module 1 – Information System Auditing Process.
In this module of the ISACA CISA certification program, you get to learn more about the concepts like IS Audit Standards, Guidelines, Codes of Ethics Business Processes, Types of Controls, Risk-Based Audit Planning, Types of Audits and Assessments, Audit Project Management, Sampling Methodology, Audit Evidence Collection Techniques, and a lot more.
Module 2 – Governance and Management of ITModule 1: Information Security Governance.
Part A: Enterprise GovernancePart A: Information Risk Assessment
Part A: Incident Management Readiness
































Master’s in Cyber Security is designed by SMEs with 12+ years of experience. Once you complete the course and carry out all the projects successfully, you will receive a master’s degree in Cyber Security and a course completion certificate from Intellipaat and EC-Council.




Data Collection: The system needs a dataset of images or videos containing faces with labeled emotional expressions. These datasets are used to train and test the machine learning models.
Incomplete and Unreliable Information: Online reviews may lack essential medical details. Patients often do not provide complete information about their medical history, including underlying conditions, allergies, or other medications they are taking.
Predicting the height and weight of a person accurately requires more information than can be provided without specific data about the individual. Height and weight are influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Additionally, individual variations can be significant.
Determining the status of loan applicants is a critical process for financial institutions and lenders to assess the creditworthiness of potential borrowers. It involves evaluating various factors to make informed decisions about whether to approve or deny a loan application. Here are the key steps and factors.
















Estimation of Credit Risk using Data Analysis and Visualization. In this Case study, You will use the concept of Data Analysis and Visualization on a Banking Dataset to find out the Credit Risk associated with each of the borrowers. By performing this case study you can help the bank to calculate the risk associated with Loan borrowers.
Data Cleansing and enrichment for a very big Job portal. In this case study you will use the concept of Data Cleaning and processing on a Job Portal Dataset so that it could be used for further analysis, and training ML or DL Models. By performing this case study you will help the job portal to make data driven decision making and implement a variety of other AI algorithms to get detailed and deep insights.
Comparison of Dimensionality reduction methods on a Healthcare Dataset with very high dimensionality. In this case study you will use the concept of dimensionality reduction and apply various algorithms to check the information loss in each of the cases, and evaluate if the concept of dimensionality reduction is helpful or not.











The Cyber Security Master's program equips students with a wide range of valuable skills, including:
How are Learning Saint-verified certificates awarded?


"I can't express how much I've benefited from the courses here. The professors are not just knowledgeable but also incredibly supportive. The practical approach to learning has prepared me for the real world, and I'm now working at my dream tech company."

"I'm amazed by the hands-on experience I've gained during my time here. The labs, projects, and research opportunities have given me a deep understanding of engineering principles. The diverse community of students also made my college life unforgettable."

"Studying fine arts at this institution has been a transformative journey for me. The freedom to express myself through art, coupled with the guidance of talented professors, has allowed me to grow as an artist. I've showcased my work in galleries, and I owe it all to this school."

At Learning Saint, student success is at the heart of everything we do. Our programs are designed to be practical, industry-relevant, and fully outcome-driven—and our learners see the difference. Every day, thousands of students trust us to guide their career journey, and their experiences reflect the quality, support, and transformation we aim to deliver.
Students Complete Course Successfully
Users reported better learning outcomes.